Blog by Valerie
This blog idea came to me a while ago when I read an article about the revival of Deq, a traditional tattooing technique in Kurdish and some other Arabic and Northern African cultures. I had always been told you can’t be buried in a Jewish cemetery with a tattoo, and something about this tradition resonated as more ancient and true to my Sumerian roots. The article explained that Deq is a form of worship, with tattooing the skin believed to also engrave a person’s soul. It is a women’s tradition that uses breast milk and another substance (such as soot) to create the ink. (Image from Wikipedia)
Deq differs greatly from modern conceptions of tattooing. While today individuals often get tattoos for decoration or to memorialise events, people, or beliefs, deq is traditionally done to request abundance, protection, blessings, or fertility from God.
Spiritual protection is a common reason for tattooing in Indigenous science. According to Western scientist Lars Krutak of the Smithsonian, traditional cultural tattooing is done for the following reasons:
- Adornment
- Identity
- Social status
- Therapeutic/Health
- Spiritual protection/Animal mimicry
(Krutak, L. (2015). The cultural heritage of tattooing: a brief history. In Tattooed skin and health (Vol. 48, pp. 1-5). Karger Publishers.) Most of these we can relate to today, though you may be wondering what therapeutic or health tattoos are. Among our ancient ancestors are tattooed ceramic figures that are over 6000 years old found in modern day Ukraine and Romania, and a 5000 year old mummy found preserved in ice in the Italian Alps who appears to have therapeutic tattoos in places on his body that look similar to a practice in traditional Asian cultural medicines. Such tattoos tend to be at joints and in the lower back. Tattooed mummies have also been found from Egypt to Siberia to Peru, and tattooed earthenwares of human or spirit figures have been found across the world from ancient Mississippi to Japan to the Philippines.
modern day Ukraine and Romania, and a 5000 year old mummy found preserved in ice in the Italian Alps who appears to have therapeutic tattoos in places on his body that look similar to a practice in traditional Asian cultural medicines. Such tattoos tend to be at joints and in the lower back. Tattooed mummies have also been found from Egypt to Siberia to Peru, and tattooed earthenwares of human or spirit figures have been found across the world from ancient Mississippi to Japan to the Philippines.
 The word ‘tattoo’ was brought into English from James Cook’s 1770s journey to New Zealand and Tahiti, and supposedly inspired Western sailors to start a tradition of tattooing themselves to remember where they had traveled and people they missed at home. (Image of a Ta`avaha (headdress) with tattoos, Marquesas Islands, 1800s, via Te Papa from here) Though modern Polynesian tattoos differ by island and culture, generally tattoos are seen as a form of spiritual protection, cultural status symbols displaying rites of passage, and signifiers of ancestral lineage. Where tattoos are on the body, and what symbols and motifs are used, are also important as they link people to their Creation story:
The word ‘tattoo’ was brought into English from James Cook’s 1770s journey to New Zealand and Tahiti, and supposedly inspired Western sailors to start a tradition of tattooing themselves to remember where they had traveled and people they missed at home. (Image of a Ta`avaha (headdress) with tattoos, Marquesas Islands, 1800s, via Te Papa from here) Though modern Polynesian tattoos differ by island and culture, generally tattoos are seen as a form of spiritual protection, cultural status symbols displaying rites of passage, and signifiers of ancestral lineage. Where tattoos are on the body, and what symbols and motifs are used, are also important as they link people to their Creation story:
In Polynesian Mythology, the human body is linked to the two parents of humanity, Rangi (Heaven) and Papa (Earth). It was man’s quest to reunify these forces and one way was through tattooing. The body’s upper portion is often linked to Rangi, while the lower part is attached to Papa.
But tattoos have a long reputation as being lower class in Western culture due to their link with slavery and criminality, which can be traced back at least to ancient Greece and Rome, and likely to ancient Mesopotamia before then. As recently as in the 1800s in parts of Europe tattoos were being outlawed and seen as unChristian. And while the major world religions are not associated with traditional tattooing, there are exceptions, such as a Buddhist monastery in Thailand that “anchors” people into scripture with tattoos. (Image from here of Angelina Jolie). And while I can’t speak for how locals feel about Angelina’s tattoos (she was given Cambodian citizenship and adopted a child there, so she has come cultural connections), I feel uncomfortable about the amount of cultural appropriation that goes along with tattooing in
And while I can’t speak for how locals feel about Angelina’s tattoos (she was given Cambodian citizenship and adopted a child there, so she has come cultural connections), I feel uncomfortable about the amount of cultural appropriation that goes along with tattooing in  Western culture. I remember a trend some years ago of getting Chinese characters tattooed without many people even knowing or speaking the language. (I used to wonder how people weren’t scared they were lied to about what their tattoo said!) And many modern designs in Western culture have originated from those early sailors’ tattoos in the 1700s and 1800s. However, many have not, and where some celebrities like Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson express Samoan heritage through tattoos, others like Mike Tyson who is not of Maori descent has a ta moko design on his face (See this article on a history of tattooing in the U.S. by Sara Etherton). (Image from Visual log of tattoos seen on sailors in a survey done in 1809. (Ira Dye, “The Tattoos of Early American Seafarers, 1796-1818,” Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 133, no. 4 [1989]: 520-554. accessed here).
Western culture. I remember a trend some years ago of getting Chinese characters tattooed without many people even knowing or speaking the language. (I used to wonder how people weren’t scared they were lied to about what their tattoo said!) And many modern designs in Western culture have originated from those early sailors’ tattoos in the 1700s and 1800s. However, many have not, and where some celebrities like Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson express Samoan heritage through tattoos, others like Mike Tyson who is not of Maori descent has a ta moko design on his face (See this article on a history of tattooing in the U.S. by Sara Etherton). (Image from Visual log of tattoos seen on sailors in a survey done in 1809. (Ira Dye, “The Tattoos of Early American Seafarers, 1796-1818,” Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 133, no. 4 [1989]: 520-554. accessed here).
I have two tattoos. The first commemorates a flower I have a cultural connection with as well as a number, a colour, and some simples values; the second commemorates an insect I have a cultural and personal connection with. I got them both with close friends at the time during important moments in my life to mark endings/beginnings. Their placement is interesting – one on my right hip, and one on my left foot. I trust the intuition of those choices. I don’t notice them much anymore, they just feel like part of the fabric of me, and I’m thankful that though I got them when I was young, I still appreciate their presence on my body, and I have no need to be buried in a Jewish cemetery anyway.
Exercise: Reflect on any tattoos you have (or have considered getting). How do you feel about them – their aesthetic, meaning, and history? Is there anywhere you would or would not get a tattoo? Do you resonate with the idea that they connect you with your Creator or that they imprint onto your soul?
![]() If you value this content, please engage in reciprocity by living, sharing and giving.
If you value this content, please engage in reciprocity by living, sharing and giving.
 I bring this up because I find unconscious sorcery very common. I recently got to the root of a painful thought loop that’s informed my whole life and was quite surprised to find that it wasn’t intergenerational trauma as I expected, but in fact (I’m assuming unconscious) negative sorcery from a former big shot professor who had it in for my mother. I did hear stories growing up about how he had bullied her, like how when she was pregnant with me and asked for afternoon classes due to morning sickness, he gave her 8am classes instead. The belief he cursed me with was “you don’t belong here”. And I do feel it was directed at me, maybe even more than my mother, because he took great issue with a young mother having an academic career. And I made her into a mother.
I bring this up because I find unconscious sorcery very common. I recently got to the root of a painful thought loop that’s informed my whole life and was quite surprised to find that it wasn’t intergenerational trauma as I expected, but in fact (I’m assuming unconscious) negative sorcery from a former big shot professor who had it in for my mother. I did hear stories growing up about how he had bullied her, like how when she was pregnant with me and asked for afternoon classes due to morning sickness, he gave her 8am classes instead. The belief he cursed me with was “you don’t belong here”. And I do feel it was directed at me, maybe even more than my mother, because he took great issue with a young mother having an academic career. And I made her into a mother. That was his hook. But what about me? As
That was his hook. But what about me? As  So the next time you’re angry at a politician and notice yourself sending them daggered thoughts laced with negative emotion, or find yourself verbally ranting about them, stop and ask yourself how you’re using your power, and if you really intend to be cursing them. Cause what we do to others we invite into our own lives! And if you think you have been cursed, feel free to
So the next time you’re angry at a politician and notice yourself sending them daggered thoughts laced with negative emotion, or find yourself verbally ranting about them, stop and ask yourself how you’re using your power, and if you really intend to be cursing them. Cause what we do to others we invite into our own lives! And if you think you have been cursed, feel free to  (Typical image of ‘spirituality’ from
(Typical image of ‘spirituality’ from  How do we know the difference between a spiritual experience and our imagination? I have seen a lot of people struggle with this – with their minds tricking them into thinking they have encountered a Spirit, for example. For me the difference is in embodiment. And when in doubt, see if and how changes occur in your everyday life as a result of the insight or guidance you got. (Image from
How do we know the difference between a spiritual experience and our imagination? I have seen a lot of people struggle with this – with their minds tricking them into thinking they have encountered a Spirit, for example. For me the difference is in embodiment. And when in doubt, see if and how changes occur in your everyday life as a result of the insight or guidance you got. (Image from 





 Trauma’s meaning, causes and methods of healing differ by culture and
Trauma’s meaning, causes and methods of healing differ by culture and  Reconnecting to the Earth
Reconnecting to the Earth Our task as healers is to allow alchemy to occur so that sh*t we are carrying in our hearts, minds, bodies and spirits can instead turn into fertiliser for ourselves and others. By consciously choosing to move into terror and aversion/disgust when we are in a safe space, we can reconnect with lost soul parts. In doing so, we gain knowledge that expands our individual and collective understanding of ourselves and our world. This is seen as the sacred calling underlying a ‘shaman’s illness’. Trauma is seen as a spiritual offering of a huge amount of energy that can redirect us into a new identity like a phoenix rising out of ashes. Indigenous healers are called ‘medicine people’ or ‘shamans’ because through healing trauma we embody medicine by living in a wiser way and offering support to others who are struggling through similar wounds.
Our task as healers is to allow alchemy to occur so that sh*t we are carrying in our hearts, minds, bodies and spirits can instead turn into fertiliser for ourselves and others. By consciously choosing to move into terror and aversion/disgust when we are in a safe space, we can reconnect with lost soul parts. In doing so, we gain knowledge that expands our individual and collective understanding of ourselves and our world. This is seen as the sacred calling underlying a ‘shaman’s illness’. Trauma is seen as a spiritual offering of a huge amount of energy that can redirect us into a new identity like a phoenix rising out of ashes. Indigenous healers are called ‘medicine people’ or ‘shamans’ because through healing trauma we embody medicine by living in a wiser way and offering support to others who are struggling through similar wounds. The dialogue of that name was with my friend
The dialogue of that name was with my friend 
 Shona (Zimbabwean) Australian woman
Shona (Zimbabwean) Australian woman  This “mere existence” of Aboriginal people as humans worthy of dignity collapses the entire ‘legal’ foundation of the Australian nation. The High Court overturned
This “mere existence” of Aboriginal people as humans worthy of dignity collapses the entire ‘legal’ foundation of the Australian nation. The High Court overturned  When I hear
When I hear  I was raised to hold family sacred, and so processing the initial childhood betrayals, followed by the adult estrangements, has been incredibly painful. It felt like a sudden orphaning that was out of my control, a genocidal loss of everyone I deeply knew, had learned to rely on and share my life with. I am still in touch with one friend from childhood, one from middle school, and my nanny’s daughter who knew me as a baby. Though I am not close with them, it feels quite precious to me that they are still in my life and knew me when I was young. My husband and a few friends have walked with me through my estrangement and have met some of my family members, but hearing stories and seeing photos isn’t the same as having witnessed me as a child in the context of my family and seeing how far I’ve come as an adult.
I was raised to hold family sacred, and so processing the initial childhood betrayals, followed by the adult estrangements, has been incredibly painful. It felt like a sudden orphaning that was out of my control, a genocidal loss of everyone I deeply knew, had learned to rely on and share my life with. I am still in touch with one friend from childhood, one from middle school, and my nanny’s daughter who knew me as a baby. Though I am not close with them, it feels quite precious to me that they are still in my life and knew me when I was young. My husband and a few friends have walked with me through my estrangement and have met some of my family members, but hearing stories and seeing photos isn’t the same as having witnessed me as a child in the context of my family and seeing how far I’ve come as an adult. In every culture there are structures of
In every culture there are structures of  It is a big deal to estrange, and I have counselled people who have told me they were considering it that it’s like the guy who got stuck in a crevice while rock-climbing and had to saw off his arm to survive – it’s drastic and changes your life forever, and sometimes just has to be done. There’s little accurate Western scientific research about estrangement, with
It is a big deal to estrange, and I have counselled people who have told me they were considering it that it’s like the guy who got stuck in a crevice while rock-climbing and had to saw off his arm to survive – it’s drastic and changes your life forever, and sometimes just has to be done. There’s little accurate Western scientific research about estrangement, with  As with any loss, my experience of estrangement has created opportunities for a lot of self-knowledge and spiritual growth. It has given me the time and desire to do gift economy work supporting people’s healing, as well as community-building, knowledge-sharing, and our other humble activities through Earth Ethos. If I had family obligations and relationships taking up my time and energy, I would not be able to serve in this way. So you can thank my family for estranging from me, as it has gifted these insights to you today. And if you know anyone who is estranged, don’t assume that their situation can, will, or should change.
As with any loss, my experience of estrangement has created opportunities for a lot of self-knowledge and spiritual growth. It has given me the time and desire to do gift economy work supporting people’s healing, as well as community-building, knowledge-sharing, and our other humble activities through Earth Ethos. If I had family obligations and relationships taking up my time and energy, I would not be able to serve in this way. So you can thank my family for estranging from me, as it has gifted these insights to you today. And if you know anyone who is estranged, don’t assume that their situation can, will, or should change.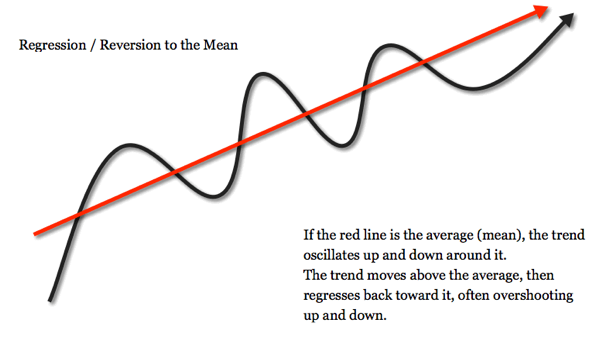 In social environments, it seems to feel proportionally less safe to be oneself the farther we identify from collective norms and ideals. There is a concept in mathematics called ‘regression to the mean’. It is basically the idea that when you put some ice into a glass of water, the ice will tend to melt and take the form of the water; in essence, it is about assimilating into a collective norm. Yet assimilation is a dirty word for many people, because we want to celebrate our uniqueness as well as being part of a peoples. (Image from
In social environments, it seems to feel proportionally less safe to be oneself the farther we identify from collective norms and ideals. There is a concept in mathematics called ‘regression to the mean’. It is basically the idea that when you put some ice into a glass of water, the ice will tend to melt and take the form of the water; in essence, it is about assimilating into a collective norm. Yet assimilation is a dirty word for many people, because we want to celebrate our uniqueness as well as being part of a peoples. (Image from  Feeling safe to celebrate our difference depends on culture and context. These social wounds keep us trapped and unable to trust ourselves, each other, non-humans, and Spirit/God/oneness. Our capacities to heal and seek retribution are also based on cultural values and intergenerational traumas. Cultures that are more welcoming of outsiders seem to encourage healing and embracing collective wounds for transformation, whereas cultures that are more exclusionary seem to ‘other’ people and tend towards separation and seeking retribution. Fear of retribution can keep us trapped and unable to trust. It is as if there is a collective trauma belief that says, ‘if we let them in, they will hurt us.’ In my experience with Judaism, and what I am learning are my deeper Sumerian cultural roots, there seems to be a collective belief that ‘we can’t trust anybody.’ My own grandmother told me that as a child, and I asked her incredulously if I couldn’t even trust her. She didn’t answer, just stared at me in silence. Living in this social environment, I never felt safe. In fact, I felt terrified to even take up space. One wrong move could find me terribly punished, kicked out of the group, or worse, judged irredeemable by God. Despite constantly striving to be ‘a good person’, it never felt like what I did was good enough. I got used to feeling terrified that threats of judgment, punishment and retribution were always imminent. I worked hard to learn the rules I might break and the triggers I might set off that would result in my being punished. But I wasn’t in control. My brother had a habit of breaking rules and refusing to admit it, so we would both be punished. This was scary, too, because I didn’t know when the punishment would happen, or how intense it would. It felt safer at times to intensely control and punish myself so that I maintained a sense of autonomy. It also seemed safest to play the part of
Feeling safe to celebrate our difference depends on culture and context. These social wounds keep us trapped and unable to trust ourselves, each other, non-humans, and Spirit/God/oneness. Our capacities to heal and seek retribution are also based on cultural values and intergenerational traumas. Cultures that are more welcoming of outsiders seem to encourage healing and embracing collective wounds for transformation, whereas cultures that are more exclusionary seem to ‘other’ people and tend towards separation and seeking retribution. Fear of retribution can keep us trapped and unable to trust. It is as if there is a collective trauma belief that says, ‘if we let them in, they will hurt us.’ In my experience with Judaism, and what I am learning are my deeper Sumerian cultural roots, there seems to be a collective belief that ‘we can’t trust anybody.’ My own grandmother told me that as a child, and I asked her incredulously if I couldn’t even trust her. She didn’t answer, just stared at me in silence. Living in this social environment, I never felt safe. In fact, I felt terrified to even take up space. One wrong move could find me terribly punished, kicked out of the group, or worse, judged irredeemable by God. Despite constantly striving to be ‘a good person’, it never felt like what I did was good enough. I got used to feeling terrified that threats of judgment, punishment and retribution were always imminent. I worked hard to learn the rules I might break and the triggers I might set off that would result in my being punished. But I wasn’t in control. My brother had a habit of breaking rules and refusing to admit it, so we would both be punished. This was scary, too, because I didn’t know when the punishment would happen, or how intense it would. It felt safer at times to intensely control and punish myself so that I maintained a sense of autonomy. It also seemed safest to play the part of  For most of my life I felt terrified to take up space. I felt like no space was ‘mine’ existentially or practically. For example, growing up, I wasn’t allowed to lock my bedroom door. I used to get dressed in my walk-in closet so I had some privacy and warning if my mother was coming into my bedroom. It took many years into adulthood – and practically ending many formational familial relationships that were untrustworthy just as my grandmother had told me – for me to become trustworthy to myself, be authentic and celebrate my difference, and surround myself with trustworthy and authentic people. By trustworthy, I mean people who say what they mean and do what they say, and when they can’t follow through on something, own it, apologise, forgive themselves, and make amends if needed. By authentic, I mean people who know their core values and practice embodying them in everyday life.
For most of my life I felt terrified to take up space. I felt like no space was ‘mine’ existentially or practically. For example, growing up, I wasn’t allowed to lock my bedroom door. I used to get dressed in my walk-in closet so I had some privacy and warning if my mother was coming into my bedroom. It took many years into adulthood – and practically ending many formational familial relationships that were untrustworthy just as my grandmother had told me – for me to become trustworthy to myself, be authentic and celebrate my difference, and surround myself with trustworthy and authentic people. By trustworthy, I mean people who say what they mean and do what they say, and when they can’t follow through on something, own it, apologise, forgive themselves, and make amends if needed. By authentic, I mean people who know their core values and practice embodying them in everyday life. It is still unsafe for me in many spaces where my values conflict with the collective. But I don’t feel a need to constantly strive towards some central ideal, nor do I feel like it’s me against the world at war. I feel peace in myself for accepting who I am and doing my best to navigate the collective morass, and for cultivating spaces where I, and others, are free to be. In this way, I can embody the knowing that we are enough. (Or ‘good enough’, whatever that means.) (Image from
It is still unsafe for me in many spaces where my values conflict with the collective. But I don’t feel a need to constantly strive towards some central ideal, nor do I feel like it’s me against the world at war. I feel peace in myself for accepting who I am and doing my best to navigate the collective morass, and for cultivating spaces where I, and others, are free to be. In this way, I can embody the knowing that we are enough. (Or ‘good enough’, whatever that means.) (Image from